ANTICARIES MECHANISM
How It Works
Functions of Medical Hydroxyapatite

The greatest achievement of Sangi’s hydroxyapatite research has been the approval of its oral care ingredient as an anti-caries agent "Medical Hydroxyapatite" (<mHAP>), in 1993.
Being almost the same as the natural hydroxyapatite of our teeth, <mHAP>works directly on tooth enamel to prevent tooth decay through three recognized actions.
As Medical Hydroxyapatite, it is also distinguished from other hydroxyapatites used as a base material or abrasive in toothpastes and is formulated only in Sangi's own products and a number of OEM products supplied by Sangi.
TRIPLE ACTION
One Substance: Three Anti-Caries Actions
Adsorption and removal of dental plaque
Nano<mHAP> adsorbs and removes plaque, the biofilm formed by oral bacteria on the tooth surface.
Hydroxyapatite’s ability to adsorb proteins is generally known, and it has long been used as an adsorbent in liquid chromatography. Its adsorption ability varies according to the method of synthesis, and <mHAP>nano-particles are particularly effective against the bacteria that cause tooth decay, especially streptococcus mutans.

Removal of plaque

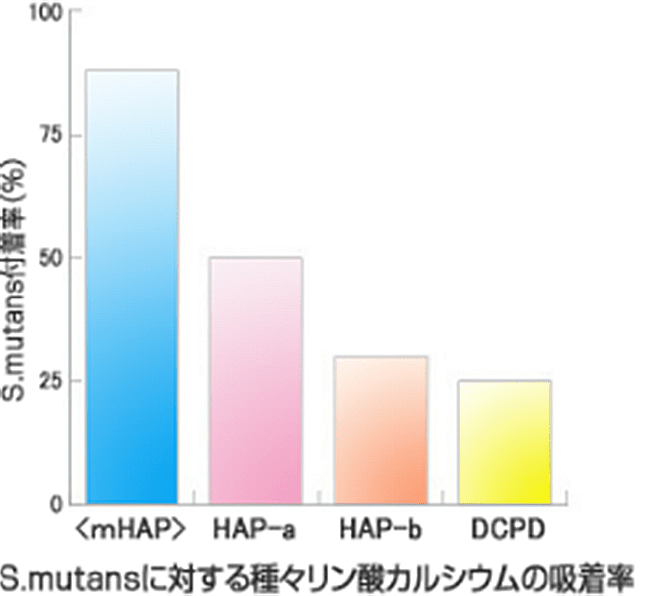
*Initial bacterial count 4.8 x 108
*Species calcium phosphate suspension 10MG/ML
Source: Study of Streptococcus Mutans Adherence to Hydroxyapatite, Kondo et al, J Dent Hlth 49(4): 614-615, 1999
(Japanese language)
Filling of micro-fissures on the tooth surface
Nano<mHAP> fills and repairs microscopic scratches on the tooth surface, making it smoother and thus more difficult for plaque and stains to reattach.
The image shows a tooth surface observed by scanning probe microscope (top surface on the left, cross section on the right).
A: Healthy tooth surface, revealing microscopic surface scratches.
B: Same enamel surface after treatment with nano<mHAP>. The surface roughness has visibly been alleviated.

Filling of surface micro-fissures


テキスト
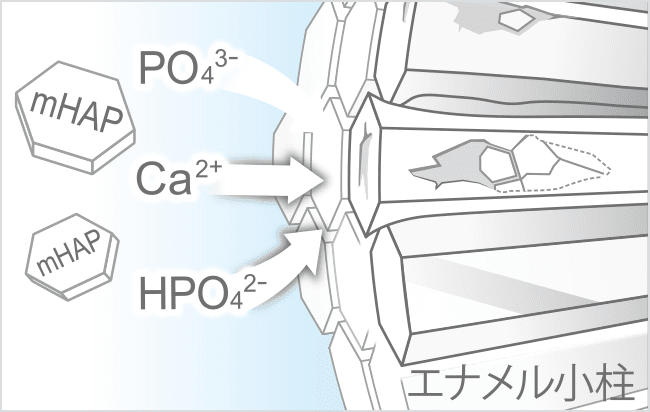
Remineralization of sub-surface demineralized areas
Nano<mHAP> remineralizes incipient caries lesions, which are the first step leading to tooth decay.
Acids from plaque bacteria and food cause minerals to dissolve out from under the surface of tooth enamel. This demineralized state is called "incipient caries", and is one step before actual tooth decay. By replenishing the minerals below the surface layer, nano<mHAP> remineralizes and protects the tooth, as shown in the data from a clinical (in situ) trial.
Subsurface remineralization

Remineralization of Early Caries by Nano-hydroxyapatite Dentifrice
K. Najibfard et al.
J Clin Dent 22(5):139-43, 2011
University of Texas Health Science Center, USA
ANTICARIES EFFECT
Preventing Decay
In the 1980s, field studies were conducted in Japanese elementary schools for the purpose of obtaining a new medical ingredient approval. The studies showed a significant difference in the rate of tooth decay in children who used a toothpaste containing nano-hydroxyapatite compared with those who used a toothpaste without the same ingredient.

Tooth decay inhibition rate
Source:Cariostatic Effect of Hydroxyapatite-Containing Dentrifices, M. Kani et al., J Dent Med 39: 809~822,1994 (Japanese language)
In one study 181 students (92 boys and 89 girls) used either a toothpaste containing Sangi’s hydroxyapatite, or a placebo without hydroxyapatite once a day after lunch for three years.
The results showed that the caries suppression rate in the hydroxyapatite group was 36% greater in boys and 56% greater in girls, than in the placebo group.


